Adaptive Data Rate (ADR) is a mechanism for optimizing data rates, airtime and energy consumption in the network.
This reference documents how ADR is implemented in The Things Stack.
How ADR Works
The ADR mechanism controls the following transmission parameters of an end device:
- Spreading factor
- Bandwidth
- Transmission power
See The Things Network LoRaWAN documentation for a general description of ADR. See the Spreading Factors section to learn how spreading factor influences data rate, range and battery life.
The Things Stack supports two ADR modes explained below - dynamic and static.
Note:
Theuse_adr and adr_margin parameters that were previously used to control The Things Stack ADR usage are now deprecated in favor of making ADR algorithm more configurable. The usage of new parameters to control ADR is explained below. To proceed with using below mentioned parameters, make sure to disable old ones using the --unset use-adr,adr-margin flag.
Dynamic Mode
Dynamic mode represents a default The Things Stack ADR mechanism. In this mode, The Things Stack calculates ADR parameters (data rate, Tx power, number of transmissions per uplink frame) values, but a user can configure the margin and min/max values for the mentioned parameters.
Before configuring this mode, it’s useful to know how it actually works, so the default The Things Stack ADR algorithm is explained below.
The Things Stack ADR Algorithm
This section describes The Things Stack ADR implementation in plain english, with links to the relevant lines of source code in our open source LoRaWAN Stack Repository.
The Things Stack ADR implementation looks at the signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) to determine the Data Rate and Tx Power, and looks at frame counters to determine packet loss, and set the number of re-transmissions accordingly.
The implementation is based on Semtech’s recommended algorithm described in this document:
- Determine the maximum SNR over recent transmissions
- Determine the minimum SNR to demodulate an uplink given the current parameters
- Calculate the margin to further optimize the data rate
- Part of this is configurable per device (if you use the CLI)
- If less measurements (uplinks) are available than necessary, include a safety margin
- Increase the data rate as long as there’s enough margin
- If there’s still margin after reaching the maximum data rate, decrease the transmit power
- Depending on packet loss, increase the number of retransmissions
Enable and Configure Dynamic Mode
To turn on The Things Stack ADR using the CLI:
ttn-lw-cli end-devices set --application-id <app-id> --device-id <dev-id> --mac-settings.adr.mode.dynamic
Values of parameters like data rate index, transmission power index and number of transmissions are calculated by the ADR algorithm, but their minimum and maximum values can be set by the user as follows:
ttn-lw-cli end-devices set --application-id <app-id> --device-id <dev-id> --mac-settings.adr.mode.dynamic --mac-settings.adr.mode.dynamic.max-data-rate-index <data_rate> --mac-settings.adr.mode.dynamic.max tx-power-index <power_index> --mac-settings.adr.mode.dynamic.max-nb-trans <nb_trans> --mac-settings.adr.mode.dynamic.min-data-rate-index <data_rate> --mac-settings.adr.mode.dynamic.min tx-power-index <power_index> --mac-settings.adr.mode.dynamic.min-nb-trans <nb_trans>
Please note that
data_ratein above and following commands is data rate index which can take values from 0-6 (referring to data rate sets DR0-DR6). For example, data rate index 0 implies using SF12 in EU868 freqeuncy plan, as explained here. You can check out detailed info for your frequency plan in the Regional Parameters specification.
Configure ADR Margin
The Things Stack Network Server calculates the ADR margin to optimize the data rate and Tx power.
Margin is the difference between the gateway’s maximum measured SNR and the minimal SNR required to demodulate a message on a given data rate. Margin is used to determine how much data rate can be increased, or how much transmit power can be lowered. Increasing the ADR margin reduces the data rate, leading to a reduced overall network capacity, but also to a lower packet loss rate in lightly loaded networks. Decreasing the ADR margin leads to a data rate increase, network capacity enhancement, but also causes higher packet loss rate.
Note:
We recommend to test the process described below on test devices before implementing it in production. It is also recommended to use different test scenarios to identify which margin best fits your environment.The Network Server uses the ADR margin of 15, but this value can be configured per device.
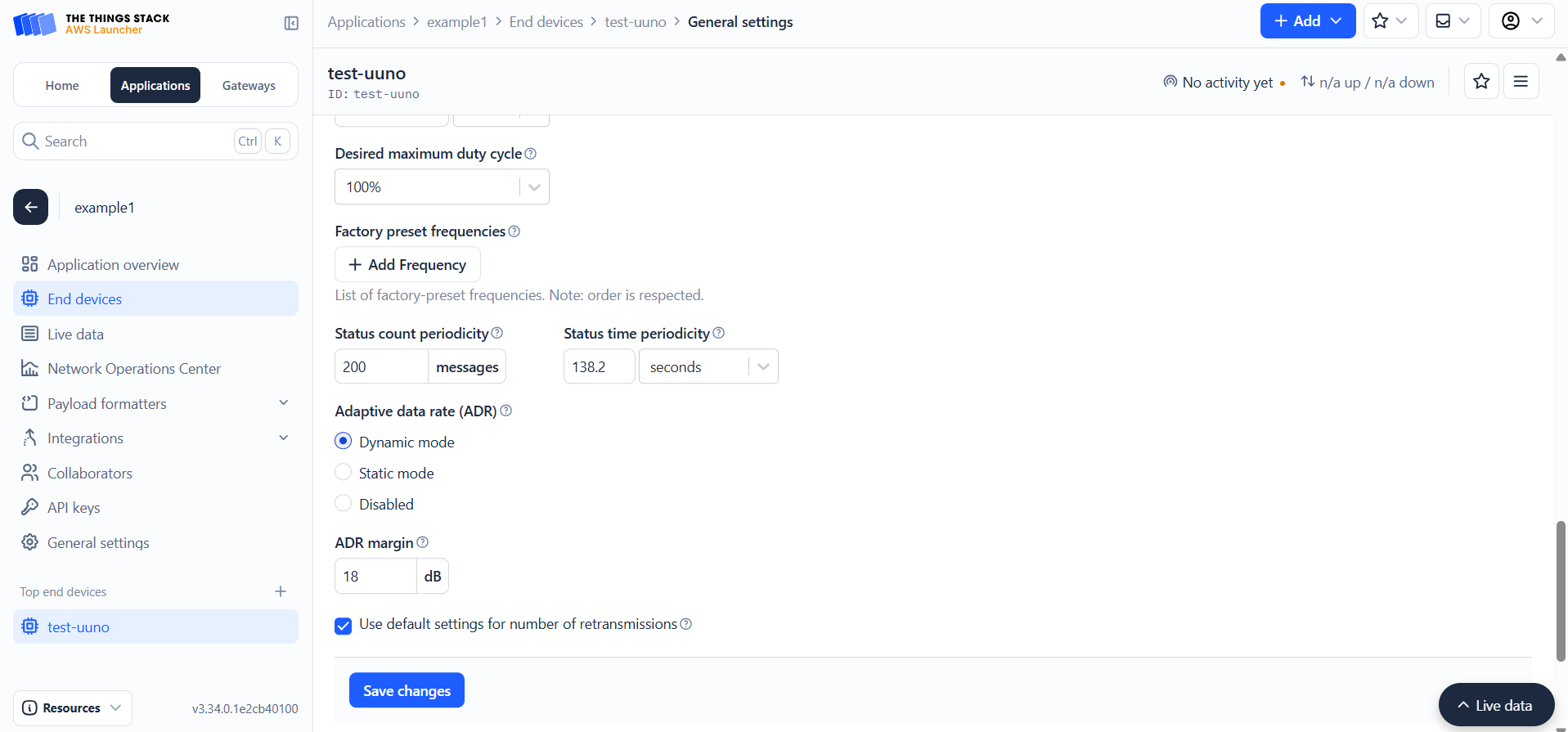
Choose the target end device and Click the Settings tab. Navigate to the Network Layer section and expand the Advanced MAC settings
Under Adaptive data rate (ADR), select Dynamic mode. Enter the value for ADR margin and click Save changes to apply.
ttn-lw-cli end-devices set --application-id <app-id> --device-id <device-id> --mac-settings.adr.mode.dynamic.margin <float32>
Since this override is part of the Network Server MAC Settings, we use the NsEndDeviceRegistry API to set this value.
| Item | Value |
|---|---|
| Endpoint | /ns/applications/{end_device.ids.application_ids.application_id}/devices/{end_device.ids.device_id} |
| Request type | PUT |
To set the ADR margin to 18 on thethings.example.com, first create a JSON file named req.json in the same folder with the following example contents.
{
"end_device":{
"mac_settings":{
"adr":{
"dynamic":{
"margin":18
}
}
}
},
"field_mask":{
"paths":["mac_settings.adr"]
}
}
The request using cURL is as follows.
curl -v -X 'PUT' -H "Content-Type: application/json" -H "Authorization: Bearer $API_KEY" \
-d @./req.json https://thethings.example.com/api/v3/ns/applications/<app-id>/devices/<device-id>
Keep in mind that changes to mac-settings.adr.mode.dynamic.<parameter> are persistent and will be present even after a device reset/rejoin. Read the MAC Settings section for detailed info.
Examples
Consider a device whose SNR values in the last 20 uplink messages were in range from 0 to 7. The data rate of the last received frame from the end device is DR3. Three cases presented below demonstrate how choosing a different ADR margin leads to different outcomes in terms of changing the data rate and Tx power.
In practice, the ADR margin value should be tuned until the optimization target is reached. The optimization target can be different (like battery duration, low packet loss, etc.) in different environments, so a user needs to decide on which margin value to adopt.
Case 1: ADR margin set to default
The default ADR margin value in The Things Stack is 15, while the minimum SNR required to demodulate a message for DR3 is 12.5.
First, the maximum SNR is computed for recent uplinks. In this example, the SNRmax is 7.
Then the SNR margin is calculated as follows:
SNRmargin = SNRmax - SNRDR3 - margindB = 7-(-12.5)-15 = 4.5
The final step is to calculate the NStep value to decide whether a data rate can be optimized:
NStep=int(SNRmargin/2.5) = int (4.5/2.5) = 1
Considering the diagram for acting on an NStep calculation depicted here, the conclusion for this example is that the Network Server should increase the data rate to DR4.
Case 2: ADR margin set to 18
The SNR margin would be:
SNRmargin = SNRmax - SNRDR3 - margindB = 7-(-12.5)-18 = 1.5
The NStep value would be:
NStep=int(SNRmargin/2.5) = int (1.5/2.5) = 0
In this case, according to the previously mentioned diagram, the Network Server should not take any action to further optimize the data rate.
Case 3: ADR margin set to 25
The SNR margin would be:
SNRmargin = SNRmax - SNRDR3 - margindB = 7-(-12.5)-25 = -5.5
The NStep value would be:
NStep=int(SNRmargin/2.5) = int (-5.5/2.5) = -1
In this case, according to the previously mentioned diagram, if Tx power is lower than its maximum, the Network Server should increase it once by 3dB, while the data rate should not be changed.
Configure Channel Steering Mode
The channel steering modes are only applicable to US915 and AU915 bands. End devices in these bands can join The Things Stack network via LoRa modulated channels with a bandwidth of 500kHz. There is one such channel within a frequency sub band (FBS), and an end device which has joined via a 500kHz channel will only use this channel for transmissions. This behavior is default, and it can be enabled as follows:
ttn-lw-cli end-devices set --application-id <app-id> --device-id <dev-id> --mac-settings.adr.mode.dynamic --mac-settings.adr.mode.dynamic.channel-steering.disabled
The end device can also be steered towards the 125kHz channels, which usually are 8 per frequency sub band (FSB), instead of using a singular 500kHz channel like mentioned above. This mode is called LoRa narrow and it can be enabled with:
ttn-lw-cli end-devices set --application-id <app-id> --device-id <dev-id> --mac-settings.adr.mode.dynamic --mac-settings.adr.mode.dynamic.channel-steering.lora-narrow
Configure NbTrans for an End Device per data rate
New in 3.30.0The Things Stack allows you fine-grained access to limit NbTrans per data rate.
In this example, we are setting the min NbTrans to 2 and max NbTrans to 3 for data rate index 5 (SF7 in EU868).
ttn-lw-cli dev set app1 eui-1231231231231231 --mac-settings.adr.mode.dynamic.overrides.data-rate-5.min-nb-trans 2 --mac-settings.adr.mode.dynamic.overrides.data-rate-5.max-nb-trans 3
{
"ids": {
"device_id": "eui-1231231231231231",
"application_ids": {
"application_id": "app1"
},
"dev_eui": "1231231231231231",
"join_eui": "1111111111111111"
},
"created_at": "2024-02-29T19:22:43.994254Z",
"updated_at": "2024-02-29T19:57:36.896606Z",
"network_server_address": "localhost",
"mac_settings": {
"adr": {
"dynamic": {
"overrides": {
"data_rate_5": {
"min_nb_trans": 3
}
}
}
}
}
}
We can now check that the changes are made.
ttn-lw-cli dev get app1 eui-1231231231231231 --mac-settings
{
"ids": {
"device_id": "eui-1231231231231231",
"application_ids": {
"application_id": "app1"
},
"dev_eui": "1231231231231231",
"join_eui": "1111111111111111"
},
"created_at": "2024-02-29T19:22:43.994254Z",
"updated_at": "2024-02-29T19:29:29.322193Z",
"network_server_address": "localhost",
"mac_settings": {
"rx2_data_rate_index": 0,
"rx2_frequency": "869525000",
"adr": {
"dynamic": {
"overrides": {
"data_rate_5": {
"min_nb_trans": 2,
"max_nb_trans": 3
}
}
}
}
}
}
Since this override is part of the Network Server MAC Settings, we use the NsEndDeviceRegistry API to set this value.
| Item | Value |
|---|---|
| Endpoint | /ns/applications/{end_device.ids.application_ids.application_id}/devices/{end_device.ids.device_id} |
| Request type | PUT |
To set the min NbTrans to 2 and max NbTrans to 3 for for data rate index 5 (SF7 in EU868) on thethings.example.com, first create a JSON file named req.json in the same folder with the following example contents.
{
"end_device": {
"mac_settings": {
"adr": {
"dynamic": {
"overrides": {
"data_rate_5": {
"min_nb_trans": 2,
"max_nb_trans": 3
}
}
}
}
}
},
"field_mask": {
"paths": ["mac_settings.adr.mode.dynamic.overrides"]
}
}
The request using cURL is as follows.
curl -v -X PUT -H "Content-Type: application/json" -H "Authorization: Bearer $API_KEY" \
-d @./req.json https://thethings.example.com/api/v3/ns/applications/test-app/devices/eui-1231231231231231
In this example, we are setting the min NbTrans to 2 and max NbTrans to 3 for data rate index 5 (SF7 in EU868).
Choose the target end device and Click the Settings tab. Navigate to the Network Layer section and expand the Advanced MAC settings
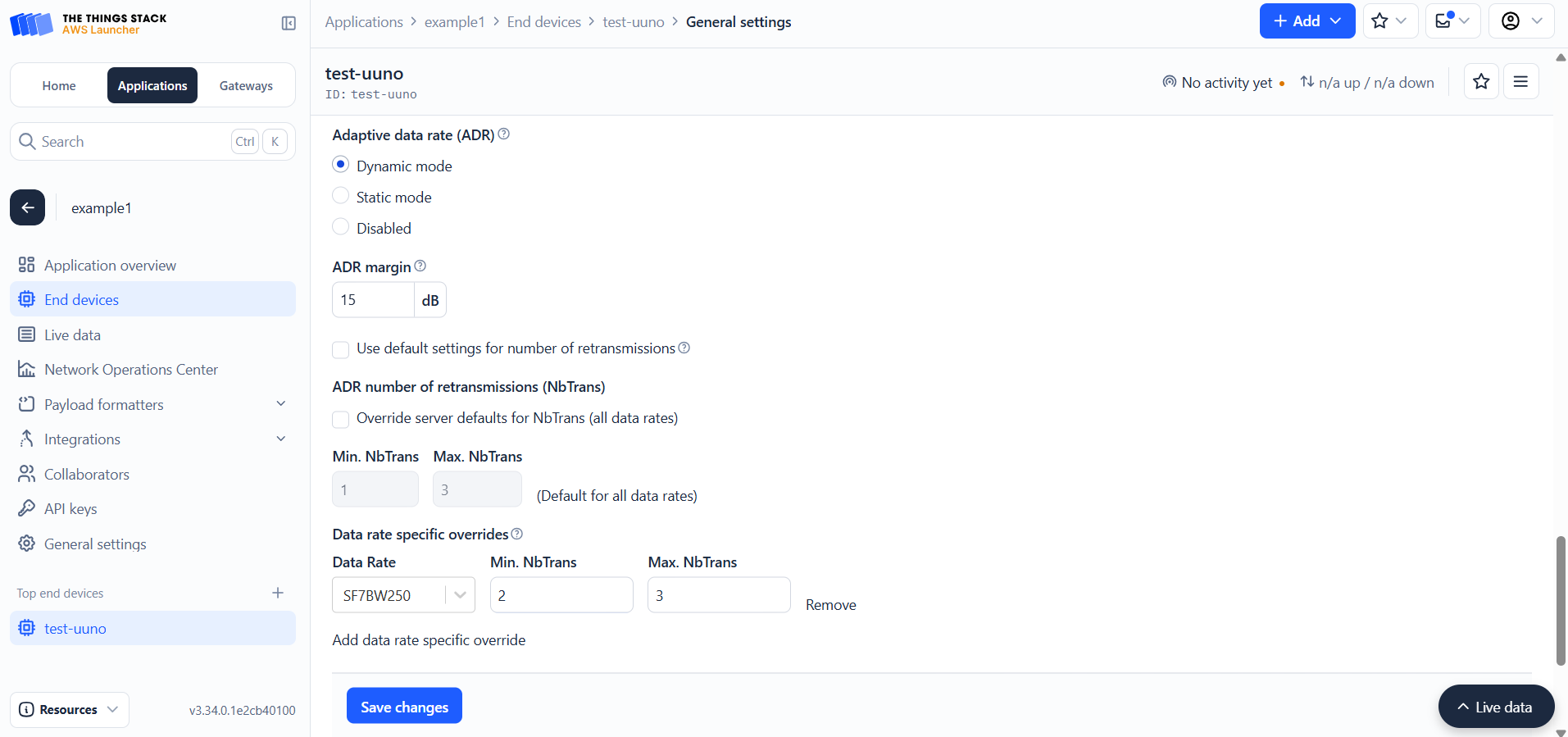
Under Adaptive data rate (ADR) select Dynamic mode. Make sure the Use default settings for number of retransmissions is unchecked.
After Expanding Add data rate specific override, select SF7BW150 Data Rate. Set the min NbTrans to 2 and max NbTrans to 3. Click Save Changes to apply.
Static Mode
Besides The Things Stack ADR mechanism described above, The Things Stack also supports using a custom ADR, meaning ADR parameters (data rate, Tx power, number of transmissions per uplink frame) can be controlled manually.
Note:
We recommend to test the process described below on test devices before implementing it in production.Before setting ADR parameters to desired values, you first need to turn off the default The Things Stack ADR mechanism. To turn off The Things Stack ADR using the CLI:
ttn-lw-cli end-devices set --application-id <app-id> --device-id <dev-id> --mac-settings.adr.mode.disabled
Please note that
data_ratein above and following commands is data rate index which can take values from 0-6 (referring to data rate sets DR0-DR6). For example, data rate index 0 implies using SF12 in EU868 freqeuncy plan, as explained here. You can check out detailed info for your frequency plan in the Regional Parameters specification.
After The Things Stack ADR mechanism is disabled, the Network Server will no longer try to optimize ADR parameters.
Now you can manually set ADR parameters to desired values using the CLI:
ttn-lw-cli end-devices set --application-id <app-id> --device-id <dev-id> --mac-settings.adr.mode.static --mac-settings.adr.mode.static.data-rate-index <data_rate> --mac-settings.adr.mode.static.tx-power-index <power_index> --mac-settings.adr.mode.static.nb-trans <nb_trans>
Static mode values that you set for ADR parameters need to be supported by the end device based on its MAC and PHY versions, and its frequency plan. Upon receiving a next uplink message, the Network Server schedules a LinkADRReq message with new ADR parameters included.
If the end device accepts all three parameters specified, then it will use them and answer with a LinkADRAns uplink message. We recommend setting all three parameters explicitly to avoid a possible rejection.
Keep in mind that changes to mac-settings.adr.mode.static.<parameter> are persistent and these values will be used even after a device reset/rejoin, until you change them.