The encodeDownlink() function is called when a downlink message with decoded payload is scheduled to be sent to the end device. The encodeDownlink() function encodes the JSON object of the downlink message to binary payload for transmission to the end device.
The decodeDownlink() function does the opposite of encodeDownlink(): it decodes the binary payload back to decoded payload.
The functions take an input object and return an output object:
function encodeDownlink(input) {
// input has the following structure:
// {
// field: "value"
// }
return {
bytes: [1, 2, 3], // FRMPayload (byte array)
fPort: 1,
warnings: ["warning 1", "warning 2"], // optional
errors: ["error 1", "error 2"], // optional (if set, the encoding failed)
};
}
function decodeDownlink(input) {
// input has the following structure:
// {
// bytes: [1, 2, 3], // FRMPayload (byte array)
// fPort: 1
// }
return {
data: {
field: "value",
},
warnings: ["warning 1", "warning 2"], // optional
errors: ["error 1", "error 2"], // optional (if set, the decoding failed)
};
}
Encoded and decoded downlink payload are incorporated in the as.down.data.receive event, where the data object contains:
{
"f_port": 1,
"frm_payload": "AQID",
"decoded_payload": {
"field": "value"
}
}
The encoded payload is in frm_payload (Base64 encoded), while the decoded payload is in decoded_payload.
If an error is present in errors, the payload is invalid and the message will be dropped. Any warnings in warnings are informative.
Note:
You can test your downlink encoder and decoder as well as schedule downlinks from The Things Stack Console.Downlink Example: The Things Node
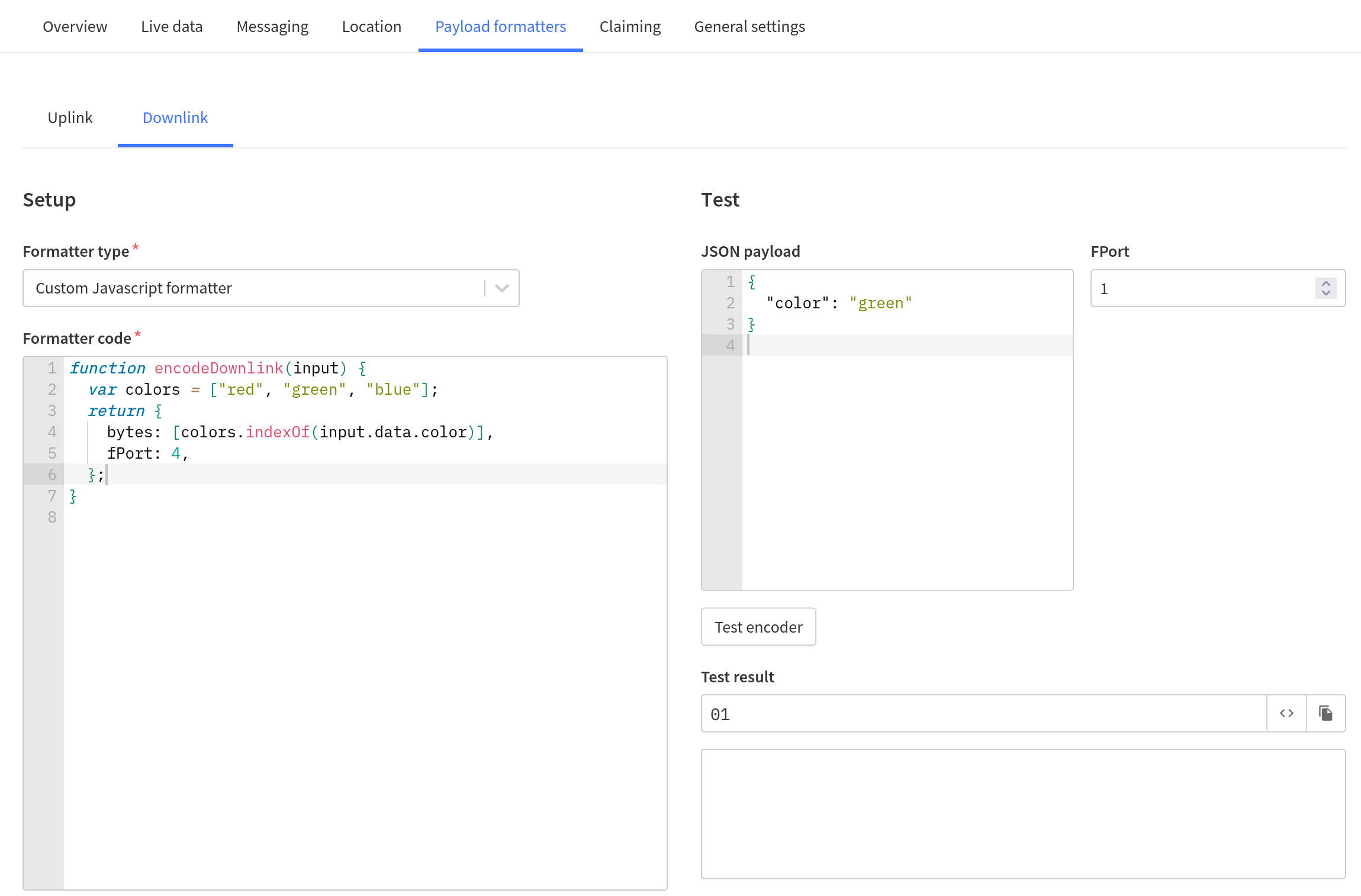
Here is an example of an encoder function that uses the color field to send a byte on a specific FPort:
var colors = ["red", "green", "blue"];
function encodeDownlink(input) {
return {
bytes: [colors.indexOf(input.data.color)],
fPort: 4,
};
}
function decodeDownlink(input) {
switch (input.fPort) {
case 4:
return {
data: {
color: colors[input.bytes[0]],
},
};
default:
return {
errors: ["unknown FPort"],
};
}
}
If the downlink with the following JSON payload is sent by the application:
{
"color": "green"
}
The output of the encodeDownlink() function will have the following structure:
{
"bytes": [1],
"fPort": 4
}
The data object of the as.down.data.receive event will therefore contain:
{
"f_port": 4,
"frm_payload": "AQ==",
"decoded_payload": {
"color": "green"
}
}